Example 1 Graph the logarithmic function f(x) = log 2 x and state range and domain of the function Solution Obviously, a logarithmic function must have the domain and range of (0, infinity) and (−infinity, infinity) Since the function f(x) = log 2 x is greater than 1, we will increase our curve from left to right, a shown below We can't view the vertical asymptote at x = 0 because itFrom the graph of f ' (x), draw a graph of f(x) f ' is negative, then zero, then positive This means f will be decreasing for a bit, and will then turn around and increase We just don't know exactly where the graph of f(x) will be in relation to the yaxisWe can figure out the general shape of f, but f we could take the graph of f that we just made and shift it up or down along the yRelated » Graph » Number Line » Examples » Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!

Parent Function Definition Examples Graphs Calculus How To
F(x) graph examples
F(x) graph examples-Consider this example Draw the graph for the quadratic polynomial function f(x) = x 2 First, for the polynomial function given here, f(x) = x 2, let us complete the table by finding the domain and the range of the function Let's fill this table by populating the values for the function f(x) by substituting the corresponding values of the Steps to Solve ln (x) We are going to use the properties of logarithms to graph f ( x) = ln ( x ) A logarithmic function has the form f ( x) = log a ( x ), and log a ( x
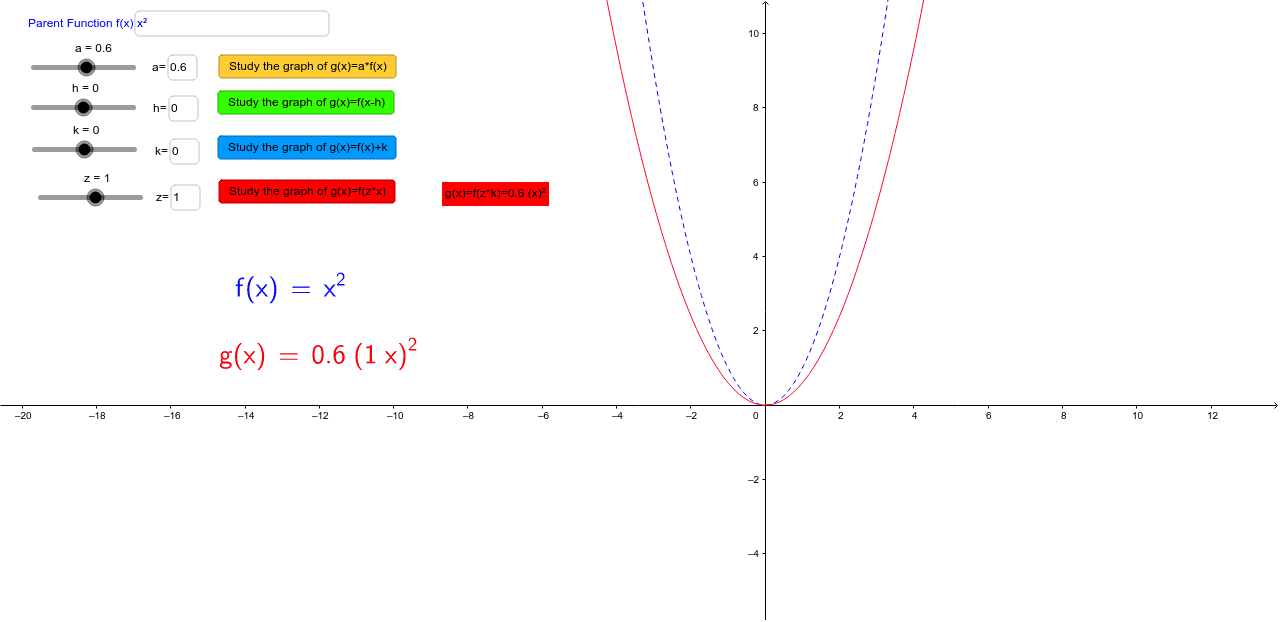



Graph Transformations Discovering Manipulating Functions Geogebra
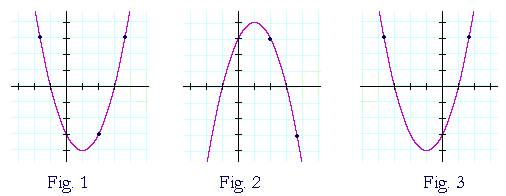
Example 1 Fig 1 is the graph of the parabola f ( x) = x2 − 2 x − 3 = ( x 1) ( x − 3) The roots −1, 3 are the x intercepts Fig 2 is its reflection about the xaxis Every point that was above the x axis gets reflected to below the x axis And every point below the x axis gets reflected above the xThe most helpful vocabulary related to your question has to do with the parity of a given function Functions are described as odd, even, neither Most functions are neither odd nor even, but it is great to know which ones are even or odd and how to tell the differenceExamples Beginning with the graphf(x)=x2, we can use the chart on theprevious page to draw the graphs off(x2),f(x Notice on the next page that the graph of is the same as the graphof our original functionx2 That's because when you flip the graph ofx2(over theyaxis, you'll get the same graph that you started with Thatx2and(
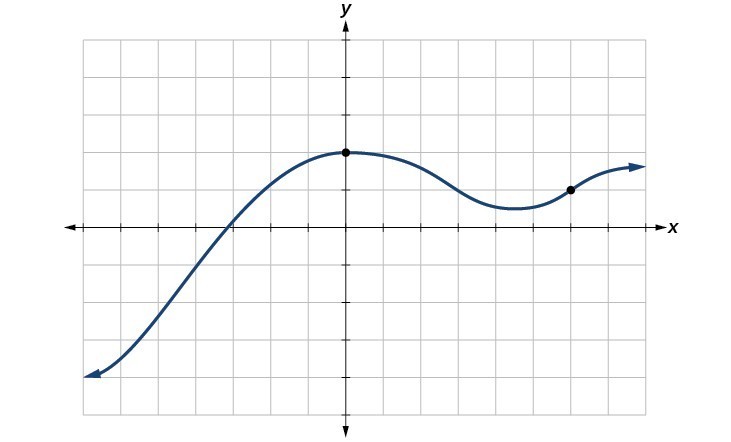
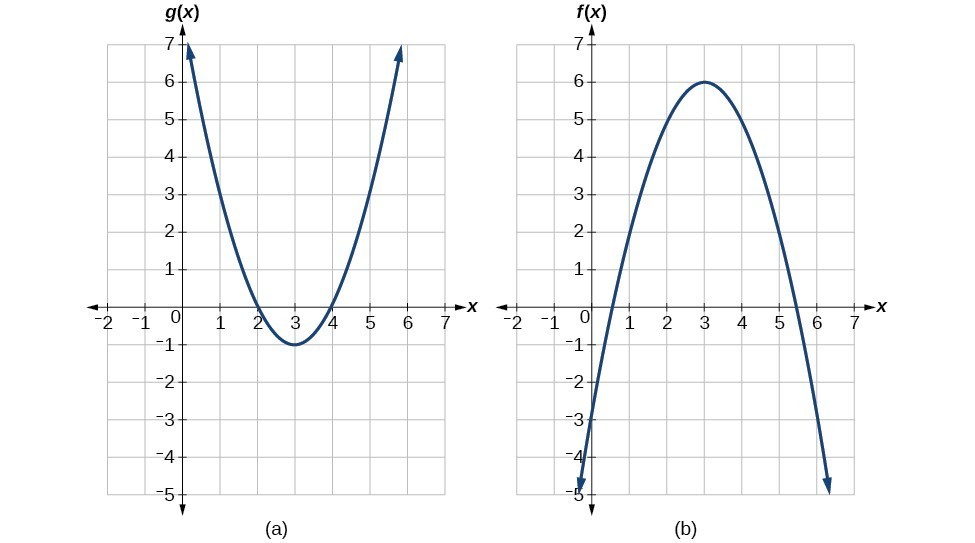
For example, the black dots on the graph in the graph below tell us that f (0) = 2 f (0) = 2 and f (6) = 1 f (6) = 1 However, the set of all points (x,y) (x, y) satisfying y =f (x) y = f (x) is a curve The curve shown includes (0,2) (0, 2) and (6,1) (6, 1) because the curve passes through those points For example, \(f(x)=x^3\) has a critical point at \(x=0\) since \(f'(x)=3x^2\) is zero at \(x=0\), but \(f\) does not have a local extremum at \(x=0\) Using the results from the previous section, we are now able to determine whether a critical point of a function actually corresponds to a local extreme value In this section, we also see how the second derivative provides informationWorked example matching a function, its first derivative and its second derivative to the appropriate graph
As an example, if I have f(x)=(x3) 3, then the graph would translate three units to the left Vertical Movement Trying to find out whether the graph would move upwards or downwards means considering the form y=f(x) ±c If c is positive, the graph moves upward If c is negative, the graph moves downward For instance, if I have f(x)=(x) 3 3, then the graph wouldIf x and y are real numbers, and if the graph of f is plotted against x, derivative is the slope of this graph at each point Slope of a linear function = The simplest case, apart from the trivial case of a constant function, is when y is a linear function of x, meaning that the graph of y is a line In this case, y = f(x) = mx b, for real numbers m and b, and the slope m is given byA function f is even f () x = fx(), x Dom()f The graph of y = fx() is symmetric about the yaxis Example 1 (Even Function Proof) Let fx()= x2 Prove that f is an even function § Solution Dom()f = x , f () x =() x 2 = x2 = fx() QED (Latin Quod Erat Demonstrandum) • This signifies the end of a proof It means "that which was to



Graphing Quadratic Functions



Discontinuous Functions
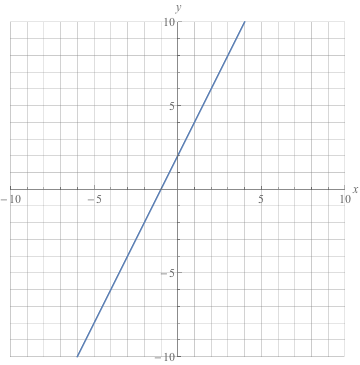
F ( 2) = 2 7 = 9 A function is linear if it can be defined by f ( x) = m x b f (x) is the value of the function m is the slope of the line b is the value of the function when x equals zero or the ycoordinate of the point where the line crosses the yaxis in the coordinate plane x is the value of the xcoordinateLinear functions have the form f(x) = ax b, where a and b are constants In Figure 111, we see examples of linear functions when a is positive, negative, and zero Note that if a > 0, the graph of the line rises as x increases In other words, f(x) = ax b is increasing on (− ∞, ∞)Hence the graph of f(x) = √ ( x 2 4) is the upper half of a circle sinsce √ ( x 2 4) is positive Hence the graph below The interval 0 , 2 represents the range of f Example 5 Find the domain, make a table of values of function f given below, graph it and find its range f( x ) = √ (x 2 9) Solution to Example 5 The domain of the function given above is found by solving x 2 9




3 2 The Derivative As A Function Mathematics Libretexts
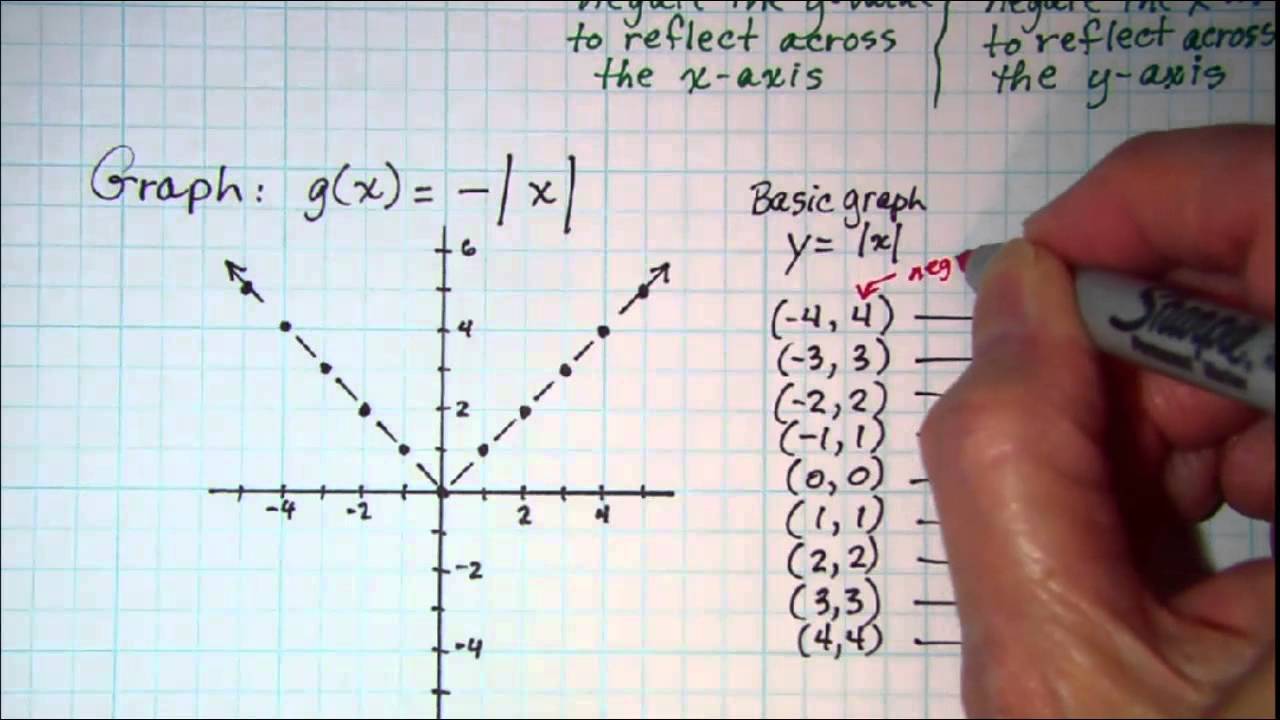



Graphing Reflections Y F X Or Y F X Youtube
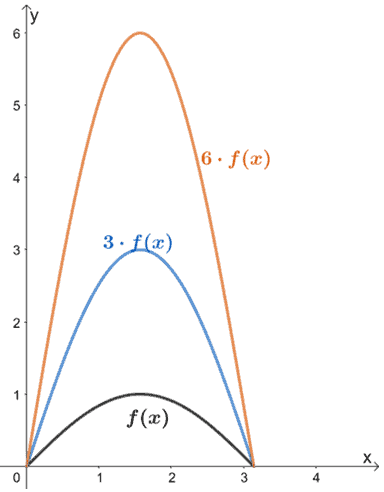
Writing graphs as functions in the form \ (f (x)\) is useful when applying translations and reflections to graphs Translations parallel to the yaxis If \ (f (x) = x^2\), then \ (f (x) a = x^2We set the denominator,which is x2, to 0 (x2=0, which is x=2) When we set the denominator of g (x) equal to 0, we get x=0 So x cannot be equal to 2 or 0 Please click on the image for a better understandingStretching a Graph Vertically or Horizontally Suppose f is a function and c > 0 Define functions g and h by g (x) = c f (x) and h (x) = f (cx) Then The graph of g is obtained by vertically stretching the graph of f by a factor of c In vertical stretching, the domain will be same but in order to find the range, we have to multiply range of



One To One Function Explanation Examples



Introduction To Limits In Calculus
Also, if there is more than one exponential term in the function, the graph may look differentThe following are a couple of examples, just to show you how they work Graph y = 3×2 –x2 Because the power is a negative quadratic, the power is always negative (or zero) Then this graph should generally be pretty close to the x axisThe modulus function y =│x│ The absolute value of x is defined as This always gives a positive result Example y=3x26x2 has graph WhereasThis example uses the basic function \(y = f(x)\) This can then be uses to draw related functions Notice that the main points on this graph are \(x = 2,\,1,\,4\) Graph of y = f(x) k Adding



Graphing The Basic Functions




Vertical And Horizontal Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
Example 5 Determine if f(x) = 2x 3 – 1 is a one to one function using the algebraic approach Solution Recall that for a function to be a one to one function, f(x 1) = f(x 2) if and only if x 1 = x 2 For us to check if f(x) is a one to one function, let's find the respective expressions for x 1 and x 2 first f(x 1) = 2 x 1 3 – 1 fF ( x) = x2 A function transformation takes whatever is the basic function f (x) and then "transforms" it (or "translates" it), which is a fancy way of saying that you change the formula a bit and thereby move the graph around For instance, the graph for y = x2 3 looks like this This is three units higher than the basic quadratic, f (x) = x2Example 2 Write the steps to obtain the graph of the function y = 3 (x − 1) 2 5 from the graph y = x 2 Solution Step 1 By graphing the curve y = x 2, we get a open upward parabola with vertex (0, 0) Step 2 Here 1 is subtracted from x, so we have to shift the graph of y = x




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



1
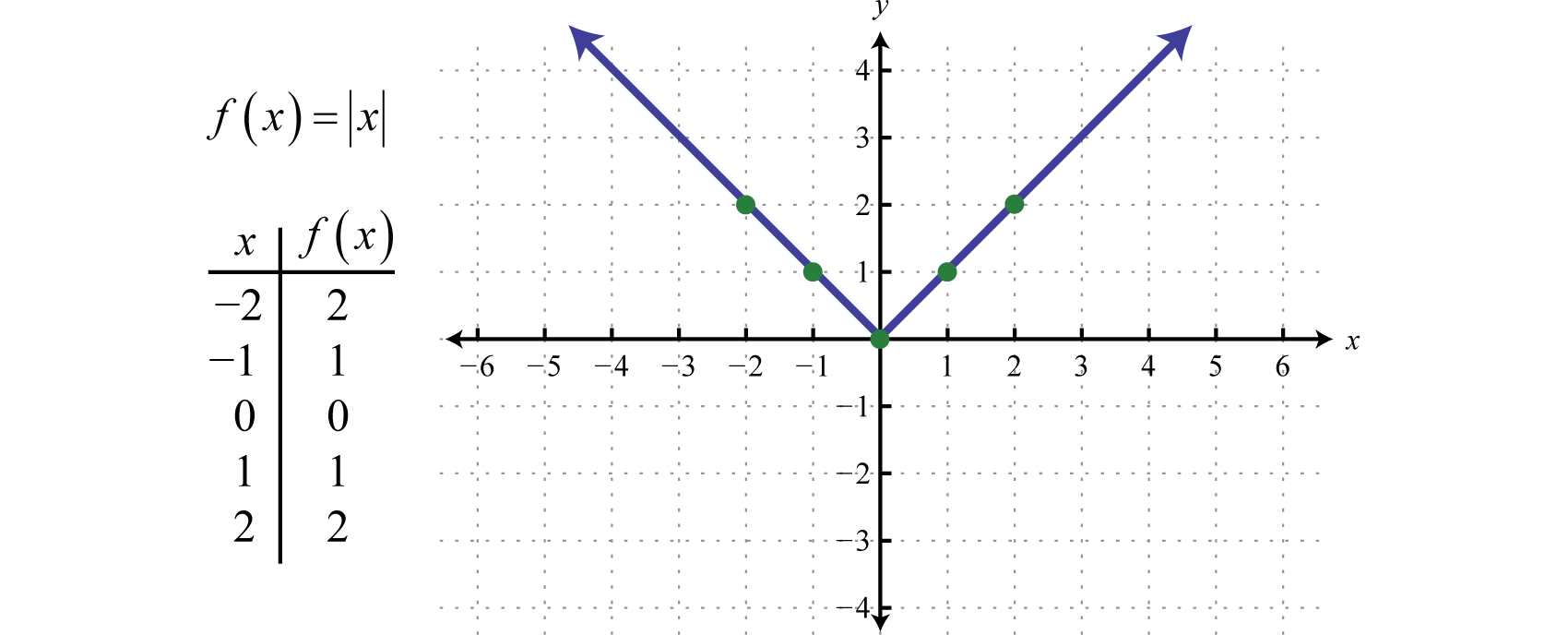
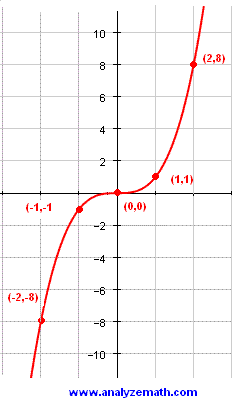
Graph of the function f(x 5) 3 from example #1 Translations But the fourth and final transformation, called a translation , is the kind we'll focus on for this lessonThe graph of f(x) in this example is the graph of y = x 2 3 It is easy to generate points on the graph Choose a value for the first coordinate, then evaluate f at that number to find the second coordinate The following table shows several values for x and the function f evaluated at those numbers x 2 1 0 1 2 f(x) 1Mathf(x)=x/math Function is giving the absolute value of mathx/math whether mathx/math is positive or negative See the y axis of graph which is mathf(x)/math against mathx/math, as x axis It shows y axis values or mathf(x




1 Graphing Functions By Plotting Points A Function F Of The Form F X Mx B Is Called A Linear Function Because Its Graph Is The Graph Of The Equation Ppt Download



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
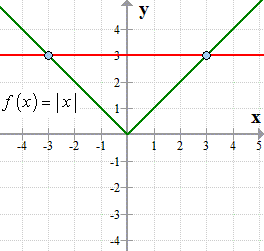
In order to find what value (x) makes f (x) undefined, we must set the denominator equal to 0, and then solve for x f (x)=3/ (x2);The graph of y = f(x) c is the graph of y = f(x) shifted c units vertically downwards g(x) = x2 2 = f(x) 2 h(x) = x2 – 3 = f(x) – 3 Look for the positive and negative sign Positive sign makes the graph move upwards and the negative sign makes it move downwards Here is a picture of the graph of g(x) = x2 1 It is obtained from the graph of f(x) = x2 by shifting it down 1 unitRemember f(x) reflects any part of the original f(x) graph that was below the xaxis in the xaxis In this video I show you how to draw graphs of the form y=f(x) using the modulus function and give you three graphs to try Examples in the video Sketch the following y



Http Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf



Graphs Of Functions
Start your free trial In partnership with You are being redirected to Course Hero I want to submit the same problem to Course Hero Cancel Proceed Correct Answer ) Let's Try Again (Try Solution Given, f (x) = 3x 2 Substituting x = 1 in f (x), f (1) = 3 (1) 2 = 3 2 = 5 Thus, the function is defined at the given point x = 1 and its value is 5 Now, we have to find the limit of the function at x = 1 Therefore, the given function is continuous at x = 1 Example 2Example 6 Graph f (x) = 1 2 x 1 and g (x) = 3 on the same set of axes and determine where f (x) = g (x) Solution Here f is a linear function with slope 1 2 and yintercept (0,1) The function g is a constant function and represents a horizontal line Graph both of these functions on the same set of axes From the graph we can see that f (x) = g (x) where x = 4 In other words, 1 2 x 1



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra



Vertical Stretch Properties Graph Examples
Algebra Examples Popular Problems Algebra Graph f(x)=(x) Rewrite the function as an equation Remove parentheses Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is , where is the slope and is the yintercept Find the values of and using the form The slope of the line is the value of , and the yintercept is the value ofExample 2 Reflections Let \textcolor{Orange}{f(x) = x^2 3x} Sketch, on the same axes, the graphs of \textcolor{Orange}{f(x)}, \textcolor{blue}{f(x)}, and \textcolor{limegreen}{f(x)} 3 marks Now, in the case of the graph f(x)= (x)^2 3(x) = \textcolor{blue}{x^2 3x}, every positive x coordinate is made negative and vice versa, and thus the whole graph is reflected inThis calculus video tutorial explains how to sketch the derivatives of the parent function using the graph f(x) This video contains plenty of examples and



Inverse Of Absolute Value Function Chilimath
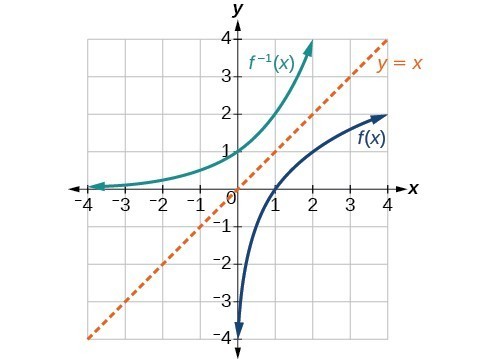



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
On the graph of a line, the slope is a constant The tangent line is just the line itself So f' would just be a horizontal line For instance, if f (x) = 5x 1, then the slope is just 5 everywhere, so f' (x) = 5 For example, if f is a function that has the real numbers as domain and codomain, then a function mapping the value x to the value g(x) = 1 f (x) is a function g from the reals to the reals, whose domain is the set of the reals x, such that f(x) ≠ 0 The range of a function is the set of the images of all elements in the domainExample If f(x) = 3x 4, find f(5) and f(x 1) f(5) = 3(5) 4 = 19 f(x 1) = 3(x 1) 4 = 3x 7 Domain and Range The domain of a function is the set of values which you are allowed to put into the function (so all of the values that x can take) The range of the function is the set of all values that the function can take, in other words all of the possible values of y when y = f(x
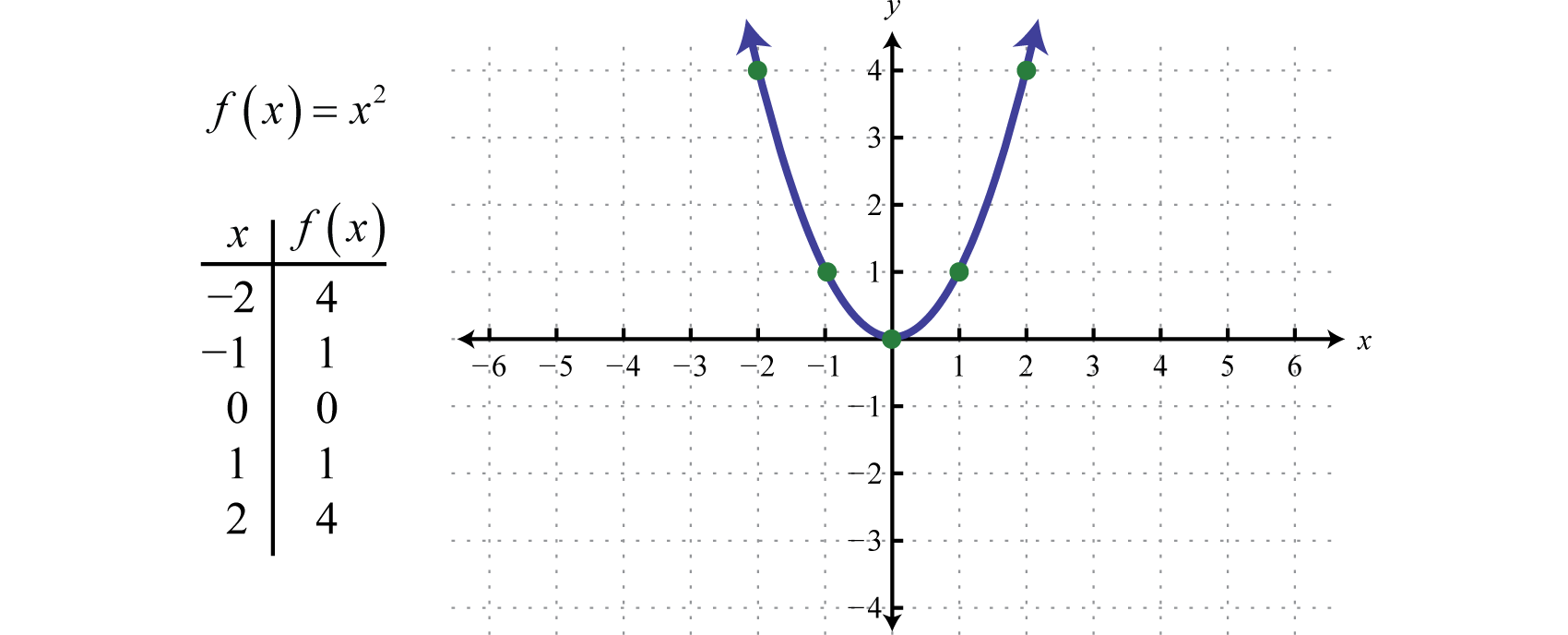



Quadratic Functions And Their Graphs




Graphing Functions With Excel
C < 0 moves it downExample Problem Graph f(x) = 4 x x f (x) −2 −1 0 1 1 4 2 16 Start with a table of values You can choose different values, but once again, it's helpful to include 0, some positive values, and some negative values Remember, 42 = = If you think of f(x) as y, each row forms an ordered pair that you can plot on a coordinate grid Plot the points Notice that the larger baseFree graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problems Mathway Visit Mathway on the web Download free on Google Play Download free on iTunes Download free on Amazon Download free in Windows Store get Go Graphing Basic Math PreAlgebra Algebra Trigonometry Precalculus Calculus Statistics Finite Math Linear Algebra Chemistry Graphing Upgrade Examples
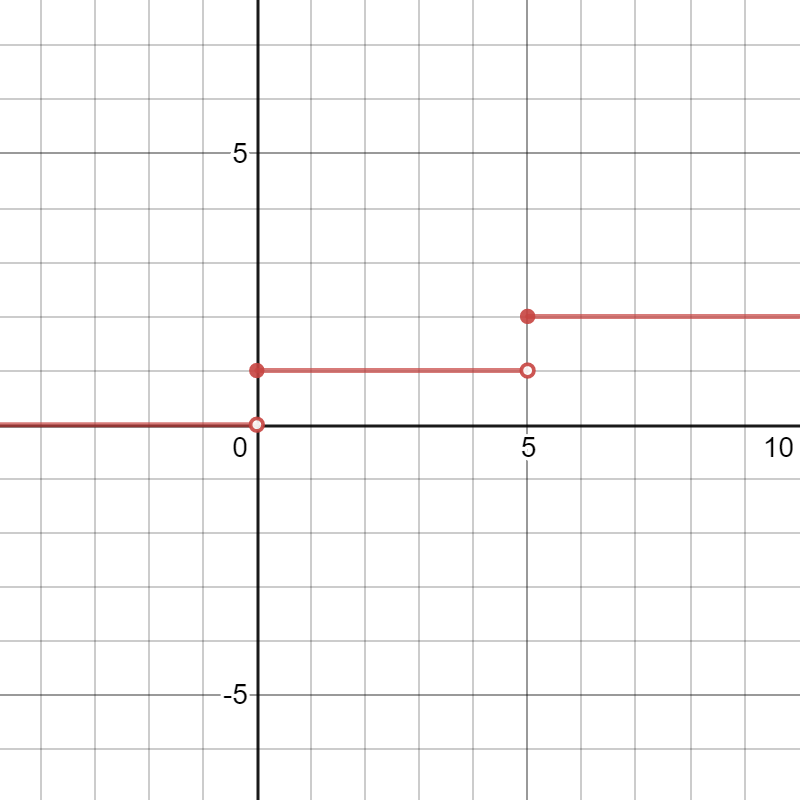



Step Functions Expii




Precalculus Shifting Reflecting And Stretching Graphs Flashcards Quizlet
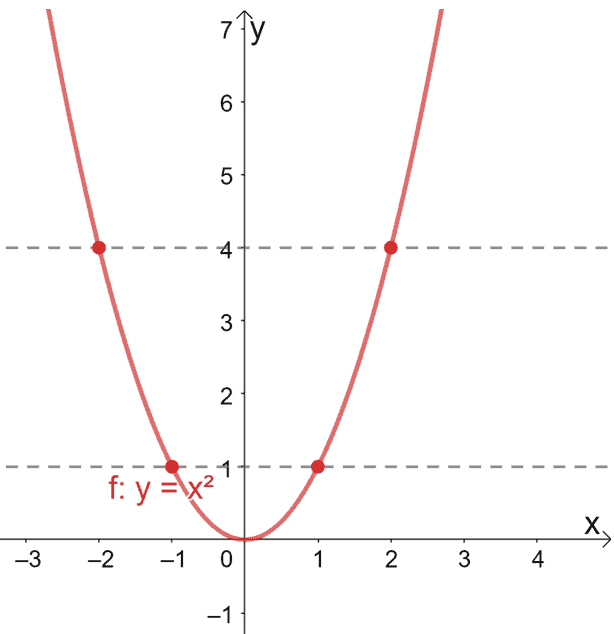
For the quadratic function f(x)=x2 f (x) = x 2, the domain is all real numbers since the horizontal extent of the graph is the whole real number line Because the graph does not include any negative values for the range, the range is only nonnegative real numbersExample 4 Graph f (x) = x Solution If x is any real number, then y = x is the greatest integer less than or equal to x ⋮ − 1 ≤ x < 0 ⇒ y = x = − 1 0 ≤ x < 1 ⇒ y = x = 0 1 ≤ x < 2 ⇒ y = x = 1 ⋮ Using this, we obtain the following graph Answer The domain of the greatest integer function consists of all real numbers ℝ and the range consists of theLet us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;




3 Ways To Graph A Function Wikihow



Transformations Mrs F X
The following video shows how to use transformation to graph reciprocal functions \(f(x) = \frac{a}{{x h}} k\) h is the horizontal translation if h is positive, shifts left if h is negative, shifts right h also shifts the vertical asymptote k is the vertical translation if k is positive, shifts up if k is negative, shifts down k also shifts the horizontal asymptote a is orientation and
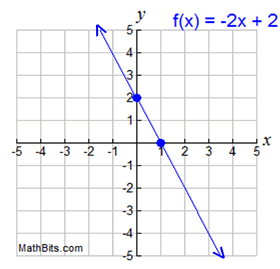



Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
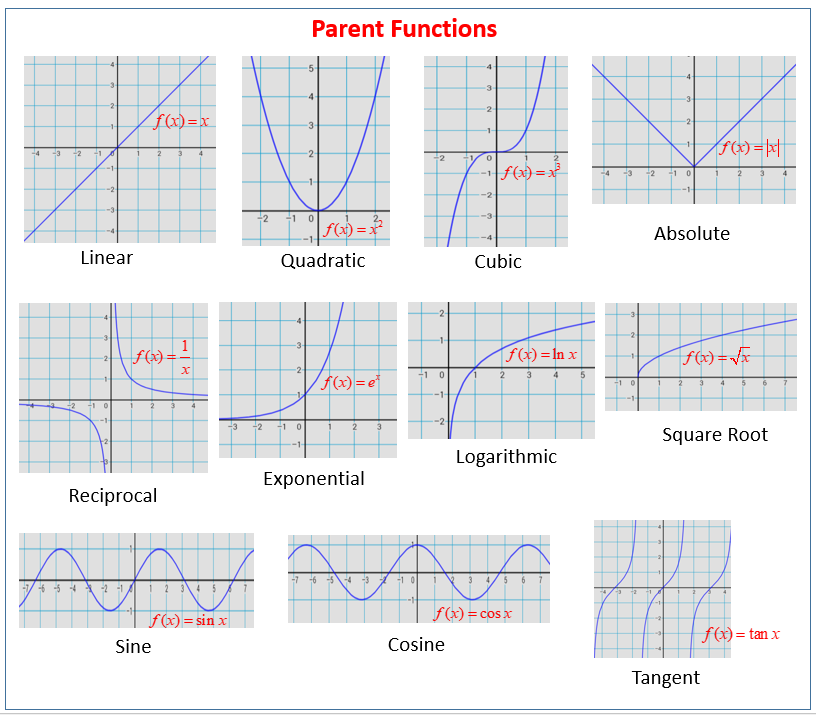



Parent Functions And Their Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Graphs Of Em F Em Em X Em And Em F Em Em X Em Examples




Graph Each Function See Examples 1 And 2 19 F X Chegg Com



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
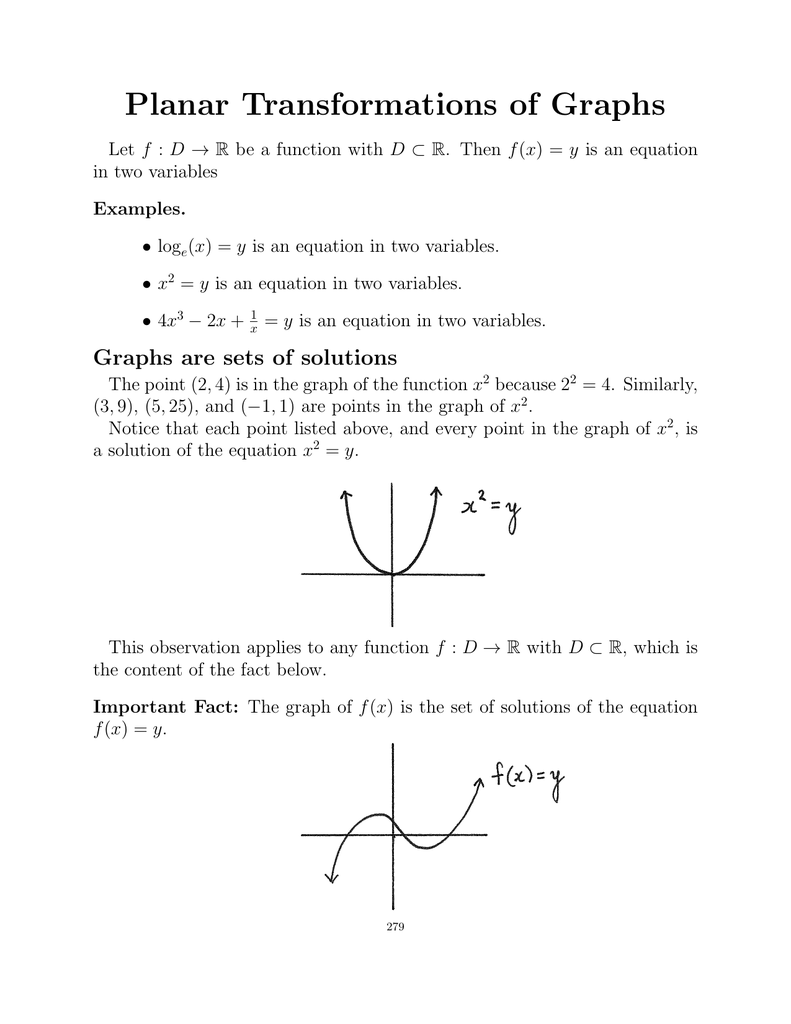



Planar Transformations Of Graphs F X F



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity




Shifting Functions Examples Video Khan Academy
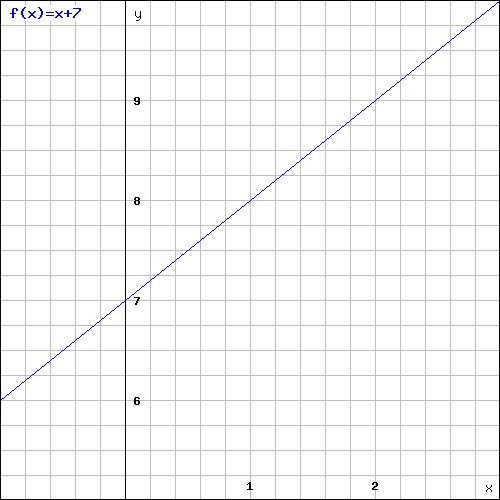



Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet



Curve Sketching



Http Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf
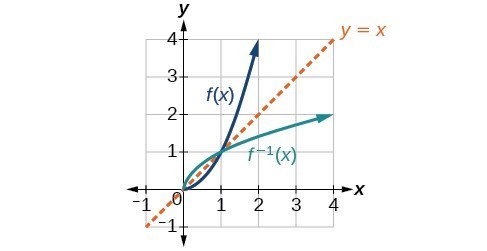



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
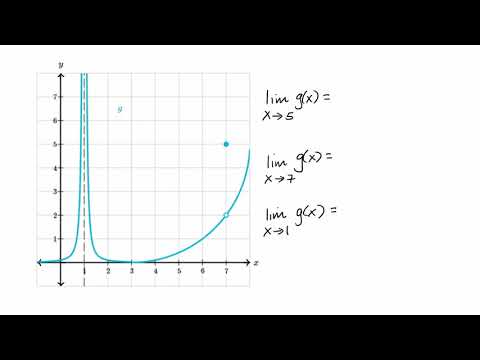



Estimating Limit Values From Graphs Video Khan Academy




The Graph Of A Function Mathcracker Com
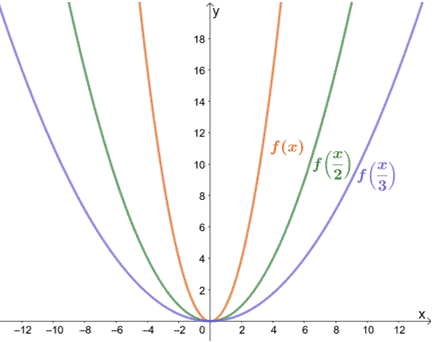



Horizontal Stretch Properties Graph Examples




Graph Transformations Discovering Manipulating Functions Geogebra




Constant Function Definition Graphs Examples



Evaluating Composite Functions Using Graphs Video Khan Academy



Asymptote



Graph Of A Function Wikipedia



Search Q One To One Function Graph Tbm Isch




Function Transformations
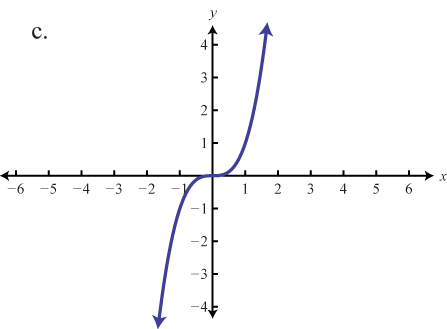



Graphing The Basic Functions




How To Sketch Moduli Functions F X F X Transformations Youtube



Reflections Of A Graph Topics In Precalculus



Parent Functions And Their Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Graphing Cubic Functions



Evaluate Composite Functions College Algebra
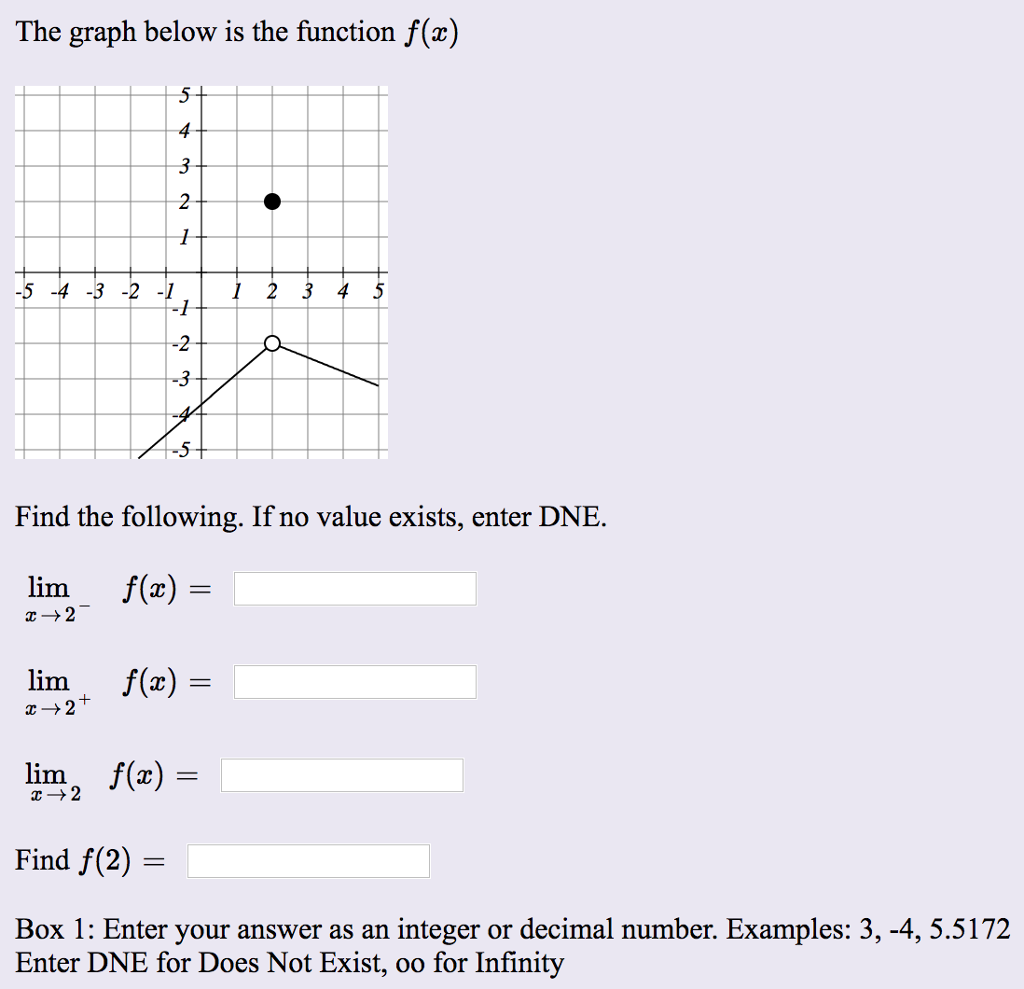



The Graph Below Is The Function F X Find The Chegg Com




Parent Function Definition Examples Graphs Calculus How To
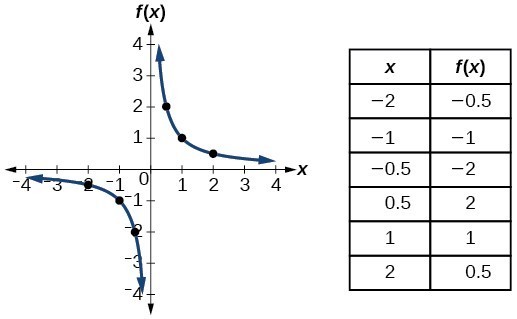



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra
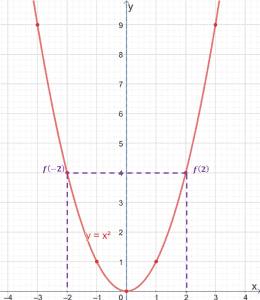



Even And Odd Functions Properties Examples



Graphing Types Of Functions
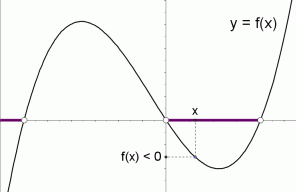



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
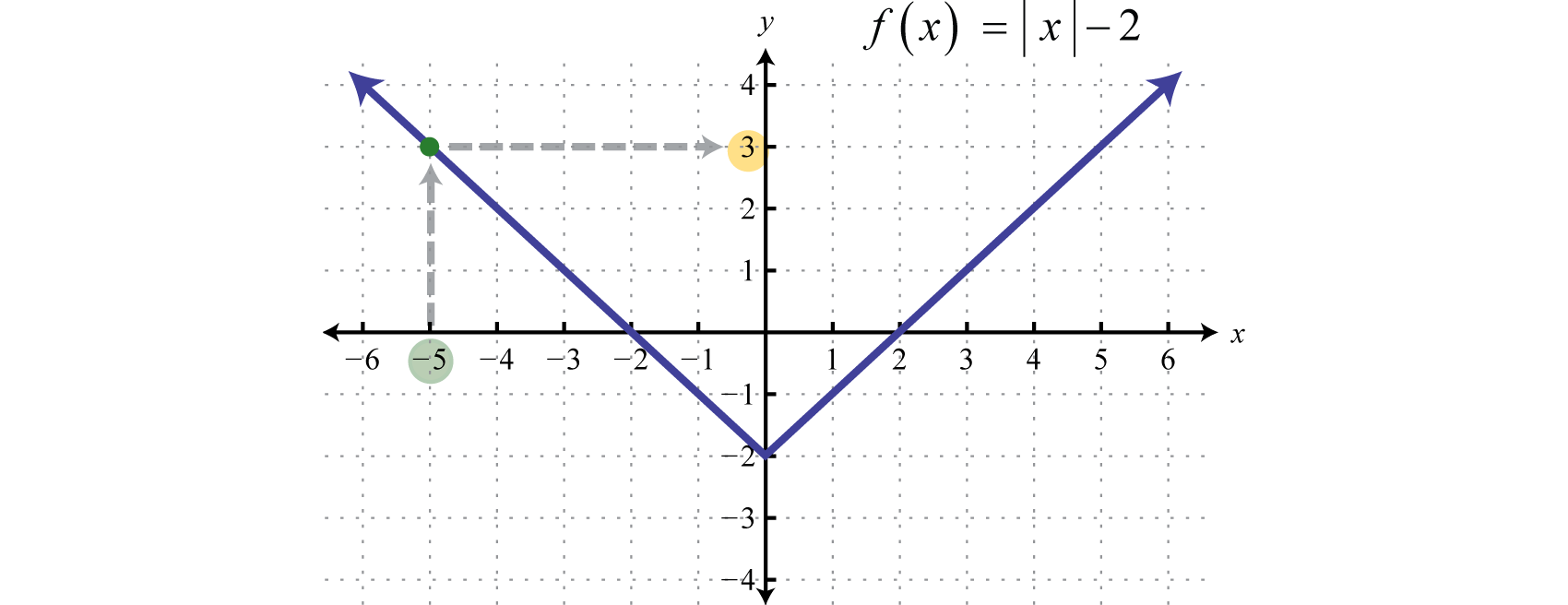



Relations Graphs And Functions
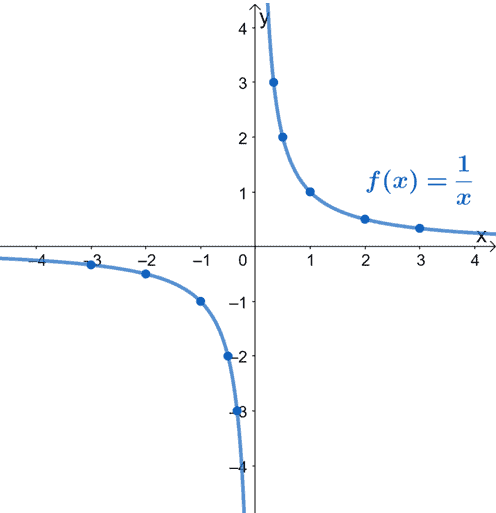



Reciprocal Function Properties Graph And Examples




Comparing Function Transformations Study Com
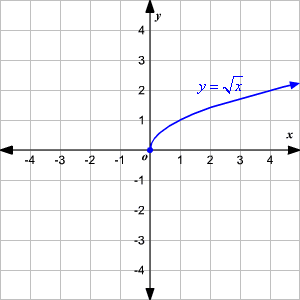



Graphing Square Root Functions
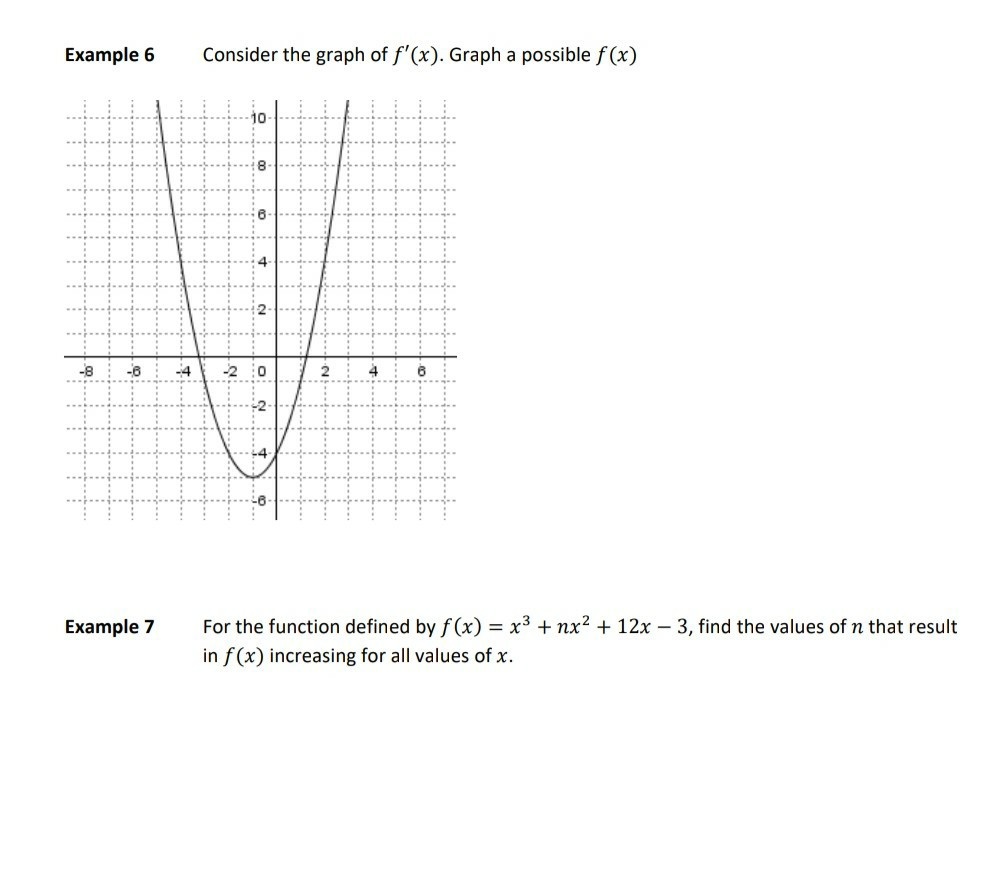



Example 6 Consider The Graph Of F X Graph A Chegg Com



Graphing Cube Root Functions
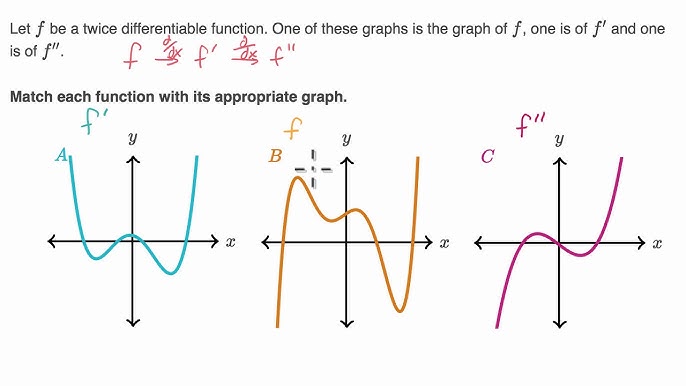



Identifying F F And F Based On Graphs Youtube
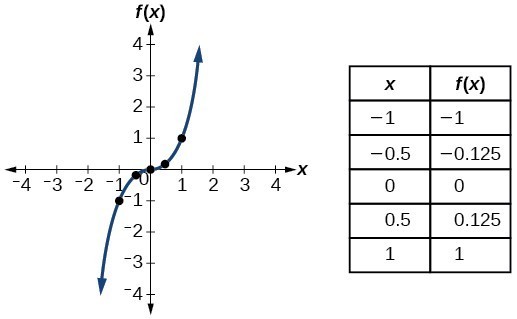



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra



Operations On Functions Translations Sparknotes



F X F X 2 F X 2
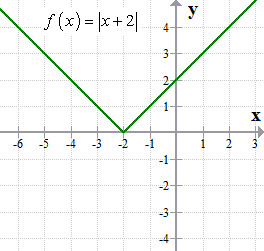



Inverse Of Absolute Value Function Chilimath




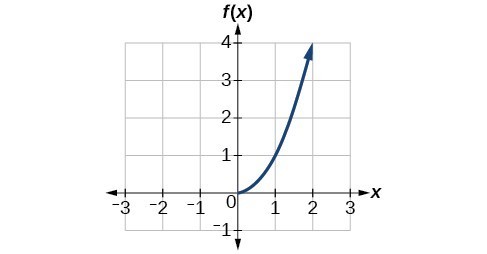
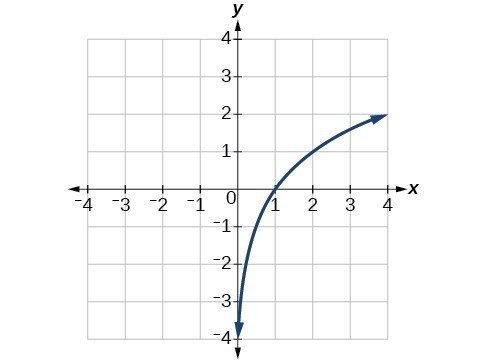
Graphs Of Logarithmic Functions Read Calculus Ck 12 Foundation



Introduction To Exponential Functions
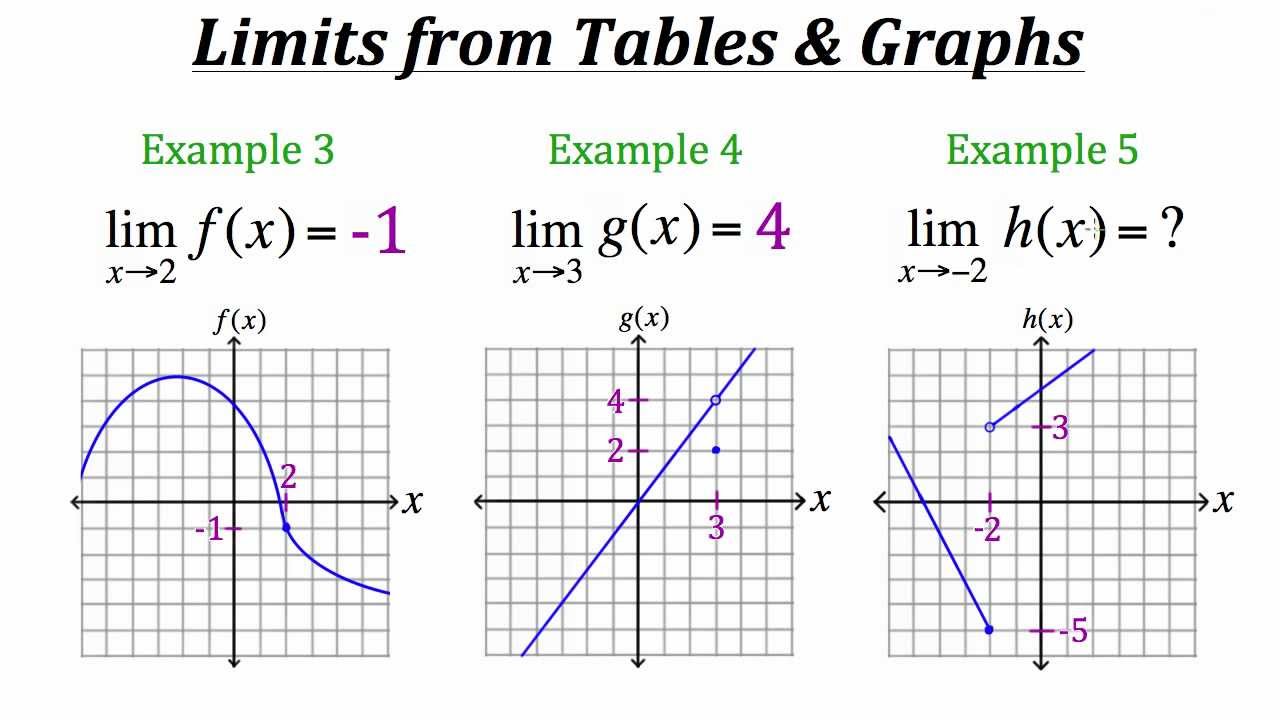



Functions Limits Of Functions From Tables And Graphs Youtube




Draw Graph Of Frac 1 F X From Graph Of F X Mathematics Stack Exchange
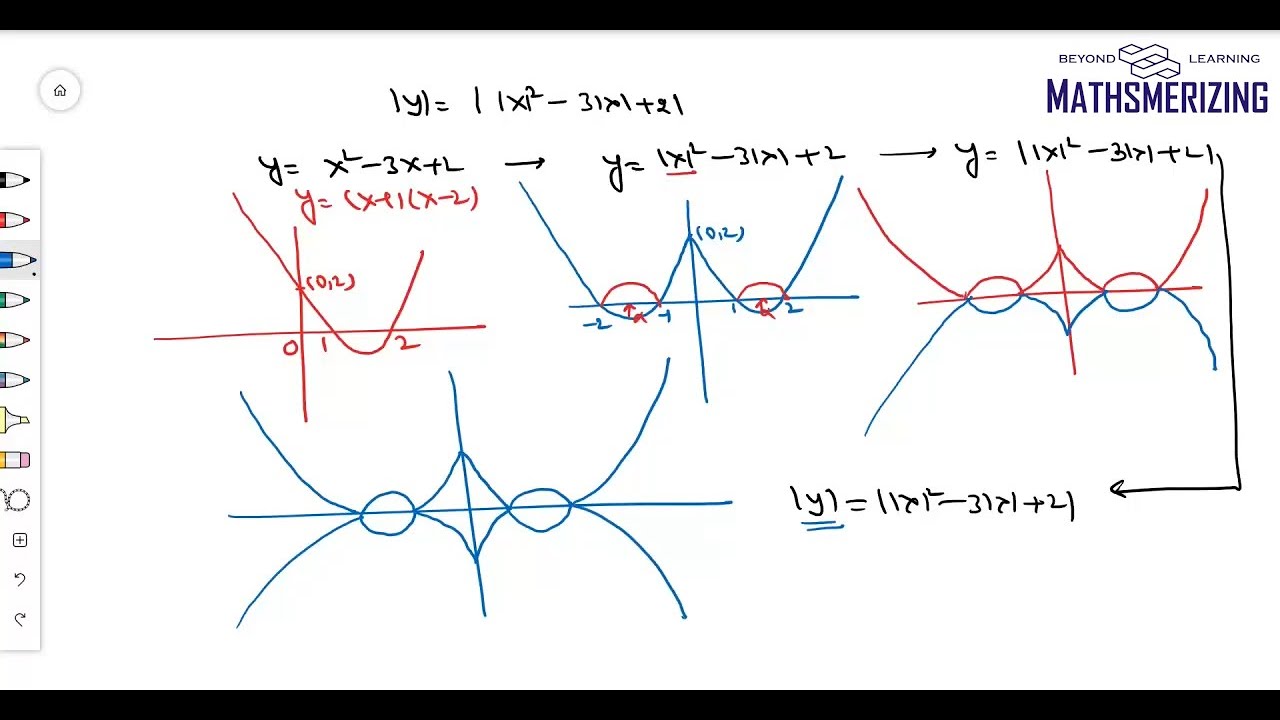



Transformation Of Graph L2 Modulus Function Graphs Of Y F X Y F X Y F X With Examples Youtube
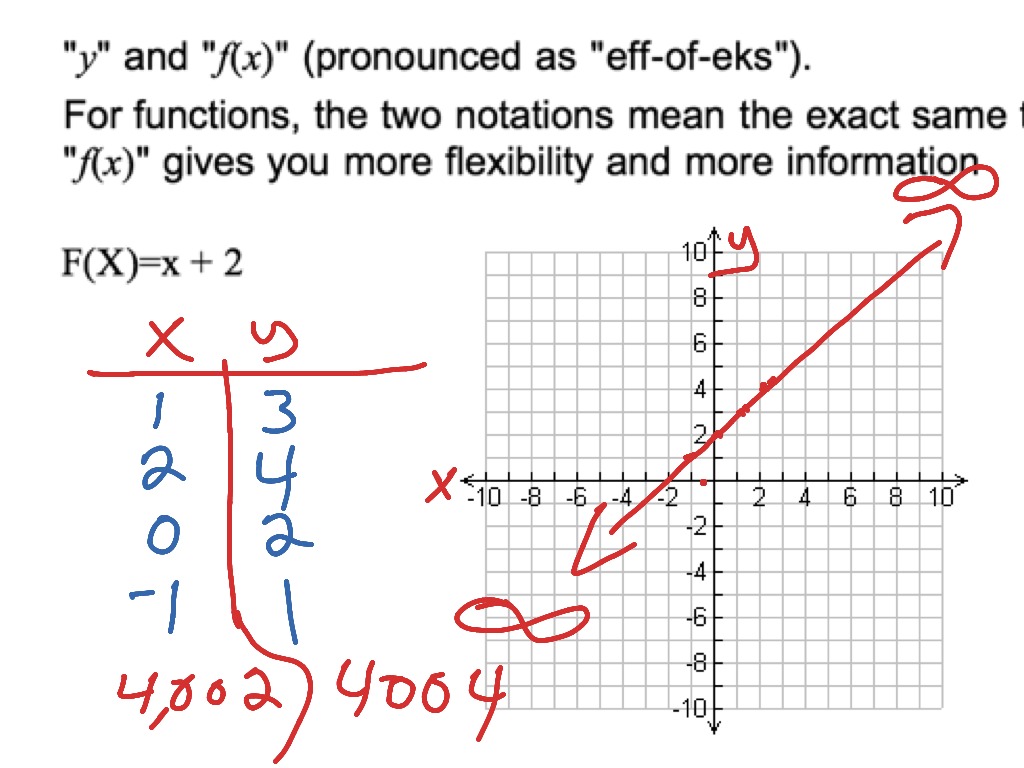



Understanding F X Function And How To Graph A Simple Function Math Algebra Graphing Functions F If 7 F If 4 Showme




Graphs Of Em F Em Em X Em And Em F Em Em X Em Examples
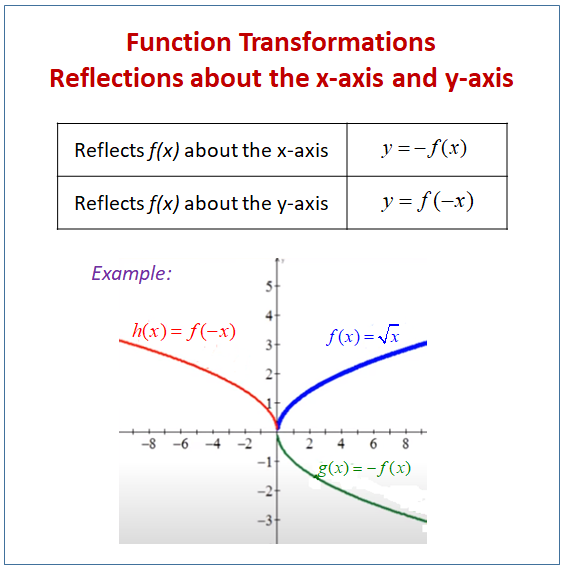



Reflecting Functions Or Graphs Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Games Activities



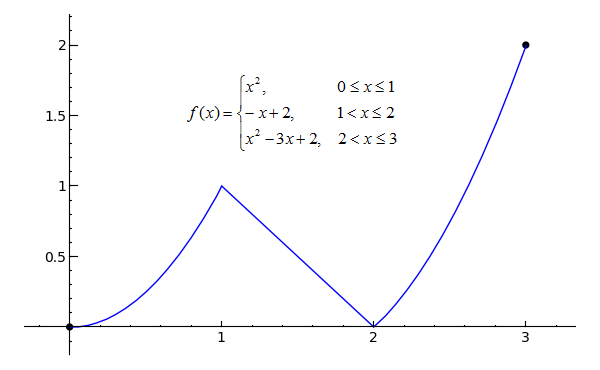
Graph Piecewise Functions
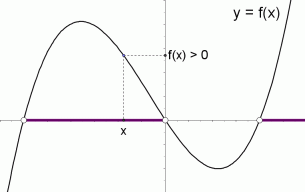



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0



Graph Transformation Y F X A Of The Function F X Youtube
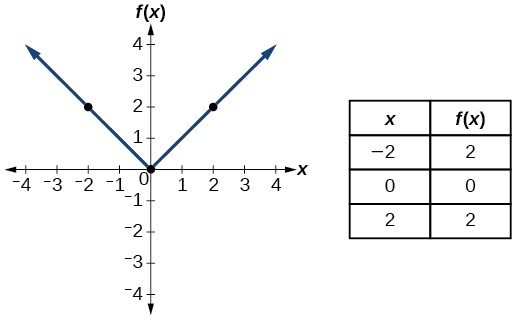



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




Matlab Plotting




Efofex Software
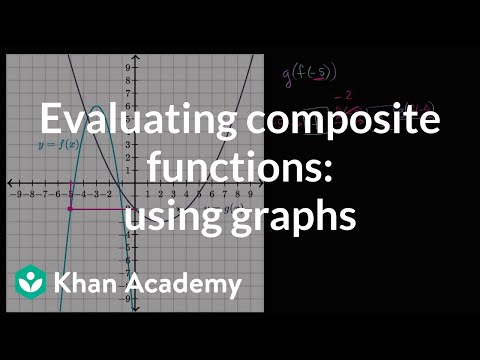



Evaluating Composite Functions Using Graphs Video Khan Academy
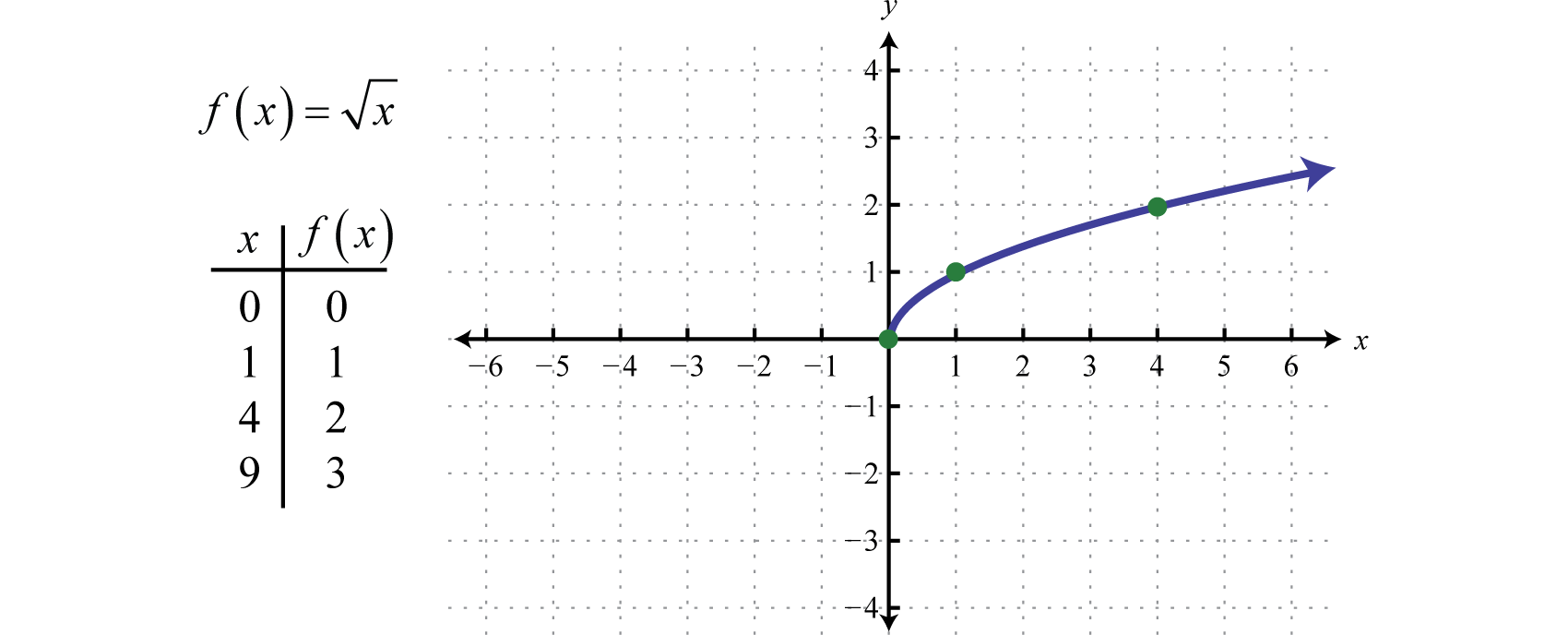



Graphing The Basic Functions



Continuous Function Conditions Discontinuities And Examples



Graphs Of Functions
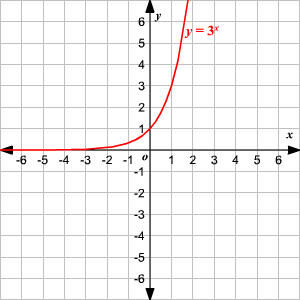



Graphing Logarithmic Functions




Estimating Limit Values From Graphs Article Khan Academy



If I Have A Graph Of A Function F X How Can I Sketch Out A Function G X 1 F X Quora
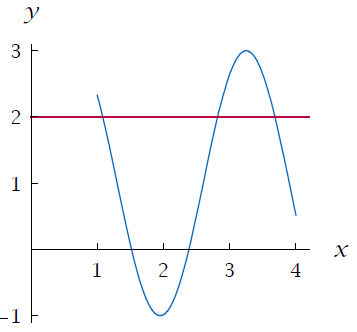



How To Check If The Function Is One To One From Its Graph
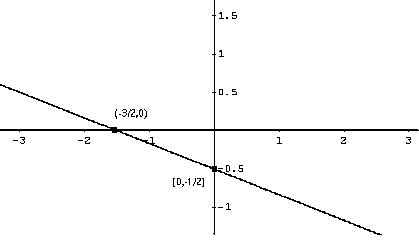



Graphing Linear Functions
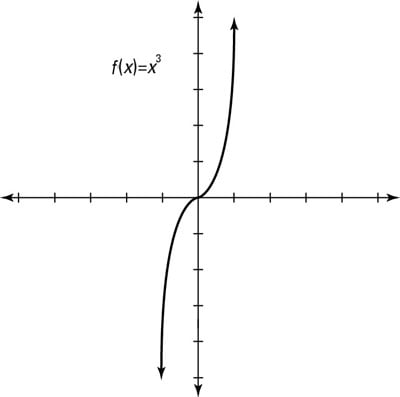



How To Identify Even And Odd Functions And Their Graphs Dummies




Graphing Reflecting Functions Study Com



1




A Graph Representing F X Of Example 3 Formulas Roots Of Complex Download Scientific Diagram



1




Graphing Quadratic Equations




What Is The Difference Between Y F X And Y F X Quora
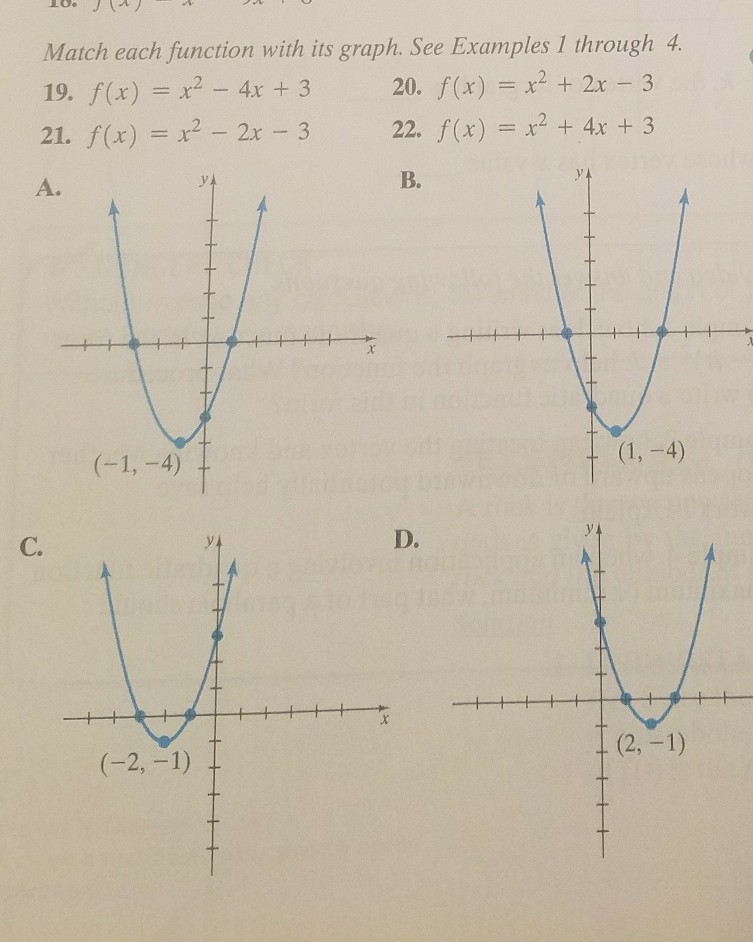



Match Each Function With Is Graph See Examples I Chegg Com



Mhf4u1 8 1 Example P2




Graphs To Find Limits Ck 12 Foundation




Graphing The Basic Functions




Example Of Area Bounded By Graph Y F X And Limits X A X B And Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿